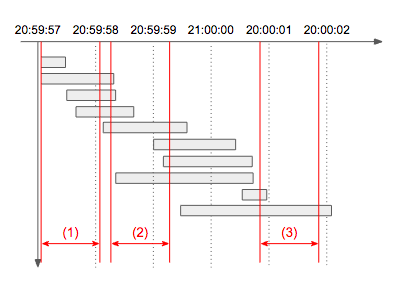
Date의 형식을 맞춰서 비교하는 방법은 아래 글을 참고하면된다.
[JAVA] Date to String / String to Date 변환(SimpleDateFormat)
프로그래밍을 하다 보면 시간이나 날짜를 사용할 일이 많은데, 아마 대부분 Date 클래스를 사용했을 겁니다. 예를 들어 현재 시간을 가져오는 코드는 다음과 같습니다. import java.util.Date; public class
readystory.tistory.com
단, parse() 메소드의 경우 ParseException을 던져주기 때문에 그에 대한 처리가 필요함.
중복for문을 이용한 방법
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(String[] lines) {
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
Date[] endDate = new Date[lines.length];
Date[] startDate = new Date[lines.length];
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) {
try {
String[] line = lines[i].split(" ");
String dateStr = line[0] + " " + line[1];
int procMilli = (int) (Double.parseDouble(line[2].substring(0, line[2].length()-1)) * -1000);
endDate[i] = format.parse(dateStr);
startDate[i] = addMilli(endDate[i], procMilli + 1);
} catch(ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < endDate.length; i++) {
int maxTemp = 0;
long endTimeMilliI = endDate[i].getTime();
long finTimeMilli = addMilli(endDate[i], 1000).getTime();
for(int j = 0; j < startDate.length; j++) {
long startTimeMilli = startDate[j].getTime();
long endTimeMilliJ = endDate[j].getTime();
if((finTimeMilli - startTimeMilli) <= 0) {
continue;
}
if(((endTimeMilliI - startTimeMilli) <= 0 && (finTimeMilli - startTimeMilli) > 0)
|| ((endTimeMilliI - endTimeMilliJ) <= 0 && (finTimeMilli - endTimeMilliJ) > 0)
|| ((endTimeMilliI - startTimeMilli) > 0 && (endTimeMilliI - endTimeMilliJ) <= 0)) {
maxTemp++;
}
}
max = Math.max(max, maxTemp);
}
return max;
}
private Date addMilli(Date date, int procMilli) {
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.setTime(date);
c.add(Calendar.MILLISECOND, procMilli);
return c.getTime();
}
}
아래는 객체 Log생성하는 방법으로 한 풀이다.
List에 Log객체를 넣어서 정렬하였다.
그리고 다른 List에는 Log의 시간값에 대하여 시작/끝 값을 넣어주었다.
정렬한 각각의 체크포인트(구간)를 이용하여, 모든 log값에 대하여 isIn 메소드를 호출한다.
Ex)
- i=1 일때 모든 log값이 체크포인트 구간내에 포함되는지 카운팅
- i=2 일때 모든 log값이 체크포인트 구간내에 포함되는지 카운팅
- ->if(카운팅값이 최댓값이면) 해당 카운팅값은 최대값으로 대입.
- i=3 일때 모든 log값이 체크포인트 구간내에 포함되는지 카운팅
- ->if(카운팅값이 최댓값이면) 해당 카운팅값은 최대값으로 대입.
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
public int solution(String[] lines) {
int answer = 0;
List<Long> checkPointList = new ArrayList<Long>();
List<Log> logList = new ArrayList<Log>();
for (String line : lines) {
Log log = new Log(line);
checkPointList.add(log.getStart());
checkPointList.add(log.getEnd());
logList.add(log);
}
Collections.sort(checkPointList);
int top = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < checkPointList.size(); i++) {
int count = 0;
for (Log log : logList) {//각 체크포인트에 대하여 Log들이 isIn인지 카운트
if(log.isIn(checkPointList.get(i), checkPointList.get(i) + 999)) {
count++;
}
}
if(count > top) {
top = count;
}
}
answer = top;
return answer;
}
class Log {
private long start = 0;
private long duration = 0;
private long end = 0;
public Log(String line) {
String[] split = line.split(" ");
String dateString = split[0] + " " + split[1];
try {
Date startDate = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS").parse(dateString);
this.end = startDate.getTime();
String[] split2 = split[2].split("s");
double parseDouble = Double.parseDouble(split2[0]);
this.duration = (long) (parseDouble * 1000);
this.start = this.end - this.duration;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public boolean isIn(long checkPointStart, long checkPointEnd) {
if(this.end < checkPointStart || this.start >= checkPointEnd) {
return false;
} else
return true;
}
public long getStart() {
return start;
}
public void setStart(long start) {
this.start = start;
}
public long getDuration() {
return duration;
}
public void setDuration(long duration) {
this.duration = duration;
}
public long getEnd() {
return end;
}
public void setEnd(long end) {
this.end = end;
}
}
}
반응형
'코딩테스트 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 자바 진수변환 알고리즘 (0) | 2021.01.25 |
|---|---|
| (2018카카오) n진수 게임 Java (0) | 2021.01.25 |
| (2018카카오) 압축 LZW 알고리즘 Java (0) | 2021.01.18 |
| (2018카카오) 후보키 Java (0) | 2021.01.14 |
| (2018카카오) 캐시 LRU(Least Recently Used) 알고리즘 Java (0) | 2021.01.14 |